the definition of valve leakage and analyze its root causes
Valve leakage is a critical issue in the operation of pipeline and industrial systems because it can lead to safety hazards, environmental damage, and economic losses. Understanding the definition and causes of valve leakage is critical to implementing effective preventive measures and maintenance practices. Let's discuss the definition of valve leakage and analyze its root causes.
Valve leakage definition:
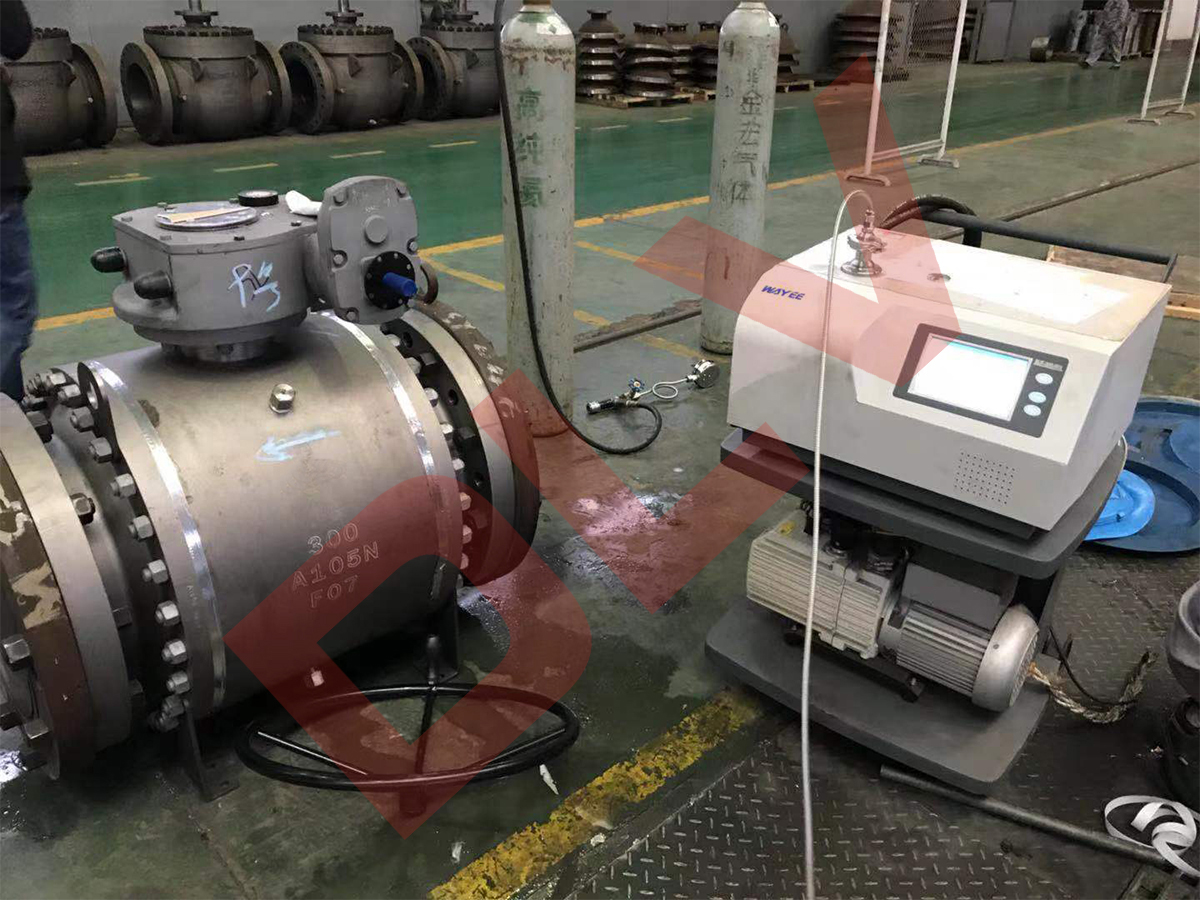
Valve leakage is the unexpected and uncontrolled flow of fluid through a valve when it is supposed to be closed or in the sealing position. This type of leakage can occur in various types of valves, including gate valves, globe valves, ball valves, and butterfly valves. Valve leaks are typically classified based on the severity of the leak, which can range from minor leaks to severe and potentially hazardous flow rates. The severity of valve leakage is often classified according to industry standards and regulations, such as ANSI/FCI 70-2 and API 598.
Reasons for valve leakage:
1. Seal Degradation: One of the main causes of valve leakage is the degradation of sealing components such as gaskets, O-rings, packing and seat seals. Over time, these components can deteriorate due to exposure to harsh operating conditions, temperature fluctuations, chemical corrosion and mechanical wear, resulting in loss of seal integrity.
2. Improper installation: Improper installation practices, including inadequate tightening of fasteners, improper alignment of valve components, and insufficient lubrication of sealing surfaces, can result in leak paths and compromised sealing performance.
3. Wear and erosion: Continuous operation of valves in abrasive or corrosive environments will cause wear and erosion of sealing surfaces, valve seats and internal components, leading to leakage over time.
4. Mechanical Damage: Physical damage to valve components (such as the stem, disc, or body) due to shock, vibration, or foreign object interference may create leak paths and compromise the structural integrity of the valve.
5. Corrosion and chemical attack: Exposure to corrosive fluids, chemical reactions and galvanic corrosion can compromise the material integrity of valve components, causing leaks and cracks in the valve structure.
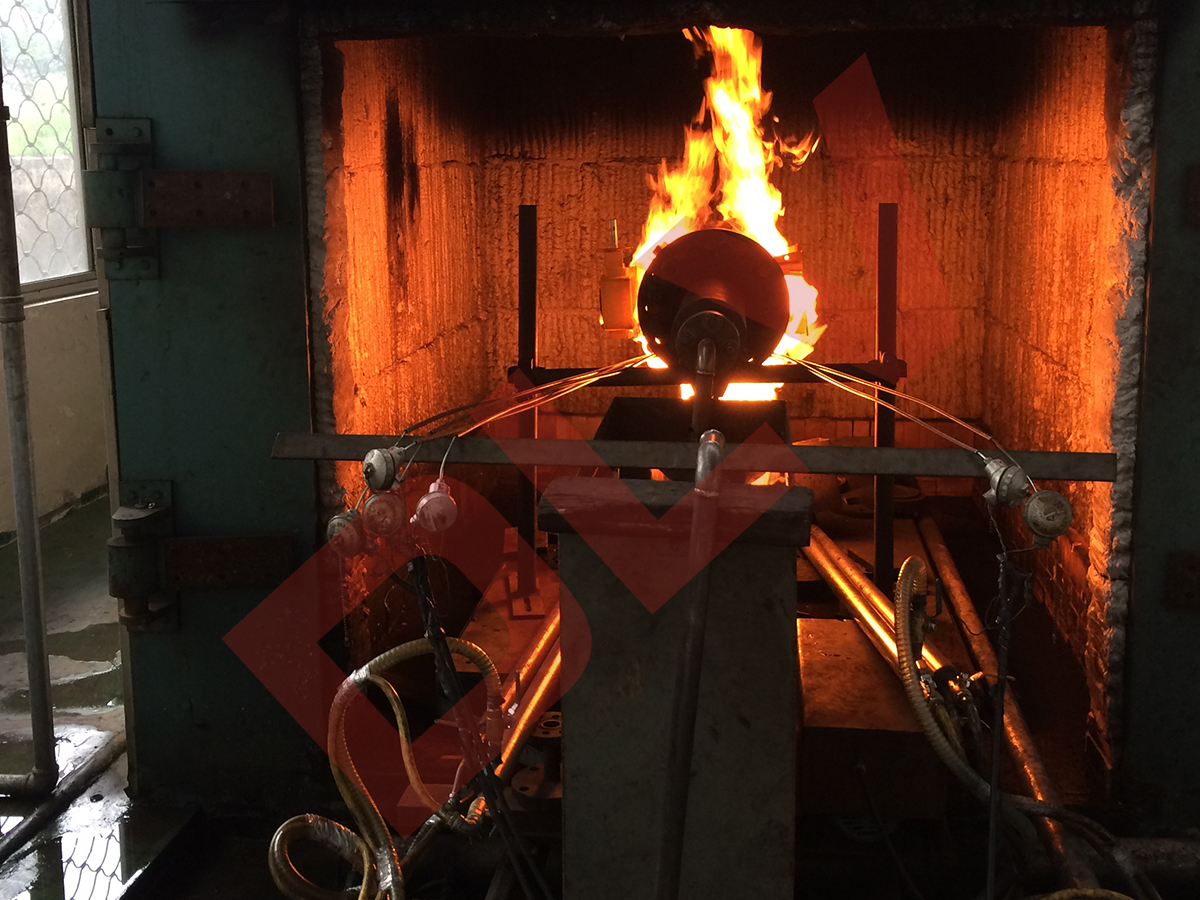
6. High Pressure and Temperature: Extreme operating conditions, including high pressure differentials and temperature changes, can impose excessive stress on valve components, potentially leading to deformation, fatigue and loss of sealing capability.
Effective maintenance practices, regular inspections, and the use of quality materials and components are critical to reducing valve leakage. Implementing preventive measures such as proper installation, routine testing and timely replacement of worn parts can help minimize the risk of valve leakage and ensure safe and reliable operation of industrial systems and pipelines.